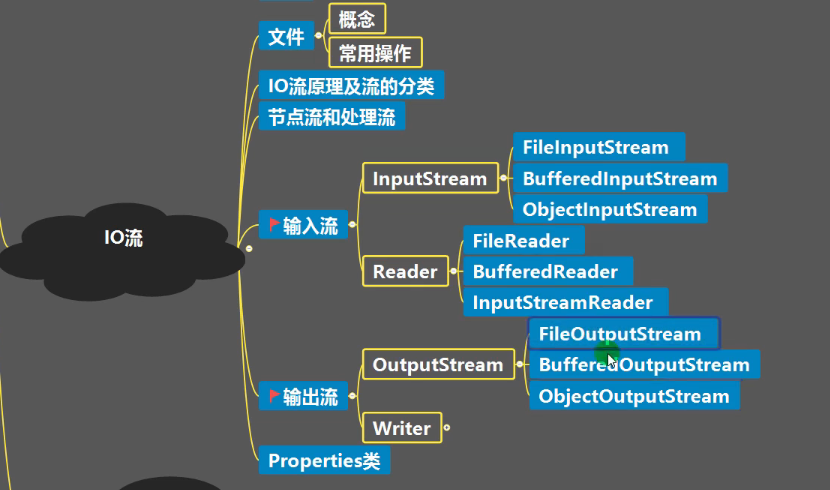
1-文件操作入门
0
Word Count: 356(words)
Read Count: 1(minutes)
—————————————————!!!注意!!!——————————————————————————————–
无论使用什么文件流,最后一定要记得 close 或者 flush
—————————==否则不会保存!!!!!!!!==———————————————————————————————–
一、文件操作
流?
—>数据从硬盘通过内存流到java程序。
1
2
3
4
5
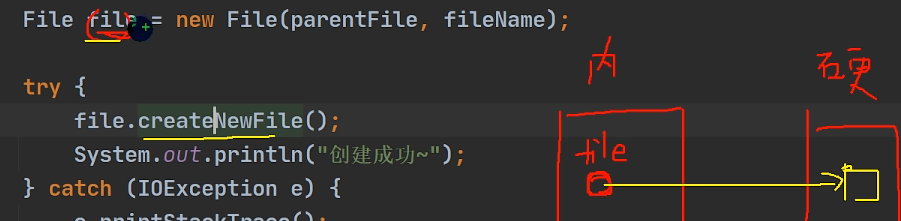
| File file = new File(filePath);
file.createNewFile();
//为什么需要第一部已经创建了对象,还要调用第二个方法
因为第一个创建的文件对象 --->存在于内存中
---->调用第二个将其写进 硬盘
|
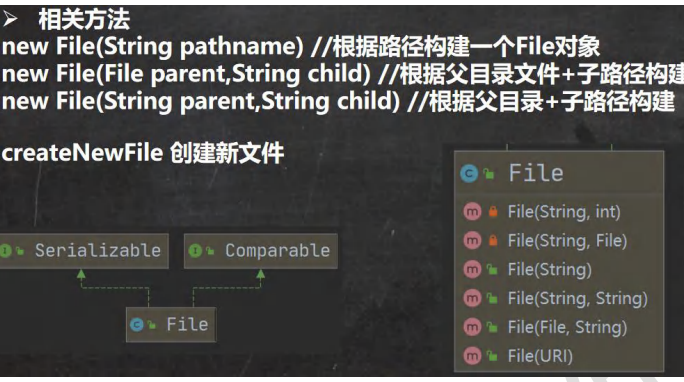
二、创建文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
@Test
public void create01() {
String filePath = "e:\\news1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void create02() {
File parentFile = new File("e:\\");
String fileName = "news2.txt";
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
韩顺平循序渐进学 Java 零基础
第 819页
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void create03() {
String parentPath = "e:\\";
String fileName = "news4.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|





